Hosts File Mac
The host file is located in the /private/etc/hosts on your MAC. Because it is situated in a protected area of the system, you cannot directly open the file and edit it. The solution is to copy the file to an unprotected location for example desktop and then make the modifications. The easiest way to find the host file is to use the Finder tool. Follow these steps to open your hosts file on Mac: Access launcher (F4 key) and type in terminal in the search field. Click on the Terminal icon. We will use Nano text editor to open the hosts file.
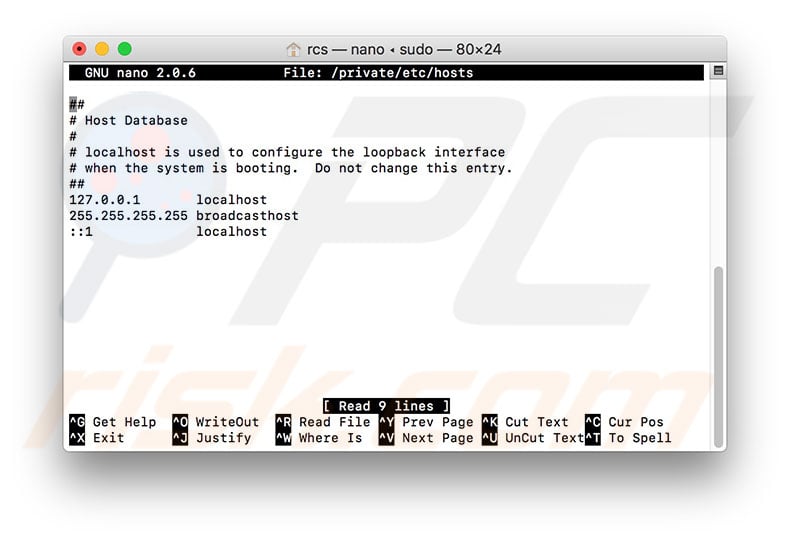
I'm trying to append a line to the hosts file on a mac. The command I'm using is: sudo echo '192.168.99.100 test' /private/etc/hosts This method does work on windows & linux but on M. The hosts file is for DNS resolution. DNS resolve names to IP addresses, and has nothing to do with ports I am afraid. You will need to use something else in conjunction with the hosts file to redirect the port (Mangle the TCP header by altering the destination port). With iptables: Does MAC OS use iptables / netfilter (I didn't think it did).?
HostsNews blog & Updates |
| Blocking Unwanted Connections with a Hosts File | ||||||||||
What it does ... You can use a modified HOSTS file to block ads, banners, 3rd party Cookies, 3rd party page counters, web bugs, and even most hijackers and possibly unwanted programs. This is accomplished by blocking the connection(s) that supplies these little gems. The Hosts file is loaded into memory (cache) at startup, so there is no need to turn on, adjust or change any settings with the exception of the DNS Client service (see below). Windows automatically looks for the existence of a HOSTS file and if found, checks the HOSTS file first for entries to the web page you just requested. The 0.0.0.0 (prefix) is considered the location of your computer, so when an entry listed in the MVPS HOSTS file is requested on a page you are viewing, your computer thinks 0.0.0.0 is the location of the file. When this file is not located it skips onto the next file and thus the ad server is blocked from loading the banner, Cookie, or some unscrupulous tracker, or javascript file. Example - the following entry 0.0.0.0 ad.doubleclick.net blocks all files supplied by that DoubleClick Server to the web page you are viewing. This also prevents the server from tracking your movements. Why? ... because in certain cases 'Ad Servers' like Doubleclick (and many others) will try silently to open a separate connection on the webpage you are viewing, record your movements then yes ... follow you to additional sites you may visit. Using a well designed HOSTS file can speed the loading of web pages by not having to wait for these ads, annoying banners, hit counters, etc. to load. This also helps to protect your Privacy and Security by blocking sites that may track your viewing habits, also known as 'click-thru tracking' or Data Miners. Simply using a HOSTS file is not a cure-all against all the dangers on the Internet, but it does provide another very effective 'Layer of Protection'. In case you're wondering ... this all happens in microseconds, which is much faster than trying to fetch a file from half way around the world. Another great feature of the HOSTS file is that it is a two-way file, meaning if some parasite does get into your system (usually bundled with other products) the culprit can not get out (call home) as long as the necessary entries exist. This is why it's important to keep your HOSTS file up to Date. Get notified of MVPS HOSTS updates. Special Note: new Windows 10 users ... the MVPS Hosts file installs just fine, no need to make any changes. Simply follow the instructions for Windows 10/8
Started providing a HOSTS file in 1998 ... and now celebrating 20 yrs. proudly still the #1 rated HOSTS file on Google ...
This download includes a simple batch file (mvps.bat) that will rename the existing HOSTS file to HOSTS.MVP then copy the included updated HOSTS file to the proper location. For more information please see the Windows version that applies to you ...
When you run the (mvps.bat) batch file - right-click and select: Run as Administrator. Once updated you should see another prompt that the task was completed. Some users may see a pop-up from certain Security programs about changes to the HOSTS file. Allow the change ... however if you see this pop-up (changes to the HOSTS file) at any other time ... investigate.

 Thanks to everyone involved for providing the online update notices for the HOSTS file. These updates are posted to most major security related sites, Newsgroups, and mailing lists, blogs etc. Get notified of MVPS HOSTS updates. Thanks to everyone involved for providing the online update notices for the HOSTS file. These updates are posted to most major security related sites, Newsgroups, and mailing lists, blogs etc. Get notified of MVPS HOSTS updates. Reproduction of information on this site, in any form, is prohibited without express written permission.
Copyright © 1998 - 2020 All rights reserved. Ever heard of host files? Most of us often confuse host files with DNS files but they’re actually pretty different. So, before we jump on understanding how to edit hosts file on Mac first let’s understand the basic difference between hosts file and DNS. Hosts File Vs DNSHosts File Mac Not WorkingMost of us are under a common impression of associating DNS with host files but the fact is they’re a lot different. DNS (Domain Name System) is basically a database or a huge directory which includes a list of which web address name belongs to which IP address. On the other hand, hosts file are localized to a specific device. So, when we’re talking about Mac hosts file it is a pretty important document which maps hostnames to specified IP addresses. This concept is actually similar to how we store contact names on our smartphone. For instance, the contact name acts as a web address and the phone number is the IP address. Editing Hosts Files on MacWhen it comes to editing hosts file on Mac, the concept is pretty simple. It’s like simply rerouting the IP address of a specific web address. We’ve often seen a message on browser saying “Cannot find the webpage which you’re looking for” right? This basically happens when a particular web address is linked to an incorrect IP address. It’s just like hitting a wrong number from your cell phone, when we try to reach a contact, the phone rings and still we ‘re unable to connect with the respective person due to incorrect entering of contact details. Here are a few important benefits of editing hosts file on Mac that’ll help you in understanding this concept in a better manner. 10 Mac Terminal Commands You Should TryBeyond macOS skin, there’s a whole another world known as Mac command line. This article will describe how to use... Mac Edit Host File TerminalBenefits of Editing Hosts File on MacOnce we reroute a web address to a specific IP address here are a few perks that you might experience: Enhanced Productivity: If you’re running a small business, then blocking a few social media websites like Facebook, YouTube, Twitter can help your employees to stay focused on their work. Network Testing: While developing a new network or developing a new website project, you can reroute the web address to a different IP address so that the real website doesn’t get affected while web development is in progress. Block Malicious Websites: If you happen to know about any malicious web sites, then rerouting these web pages to a secure landing page can prevent your system from any potential threat.  Increased Speed: As the hosts file are localized to your Mac or a specific device, finding a web page can tremendously speed up your browsing experience as compared to DNS. How to Edit Hosts File on Mac with TerminalBefore you proceed further on editing hosts file on Mac, make sure you have the administrator privileges of your device beforehand.
Also Read:- 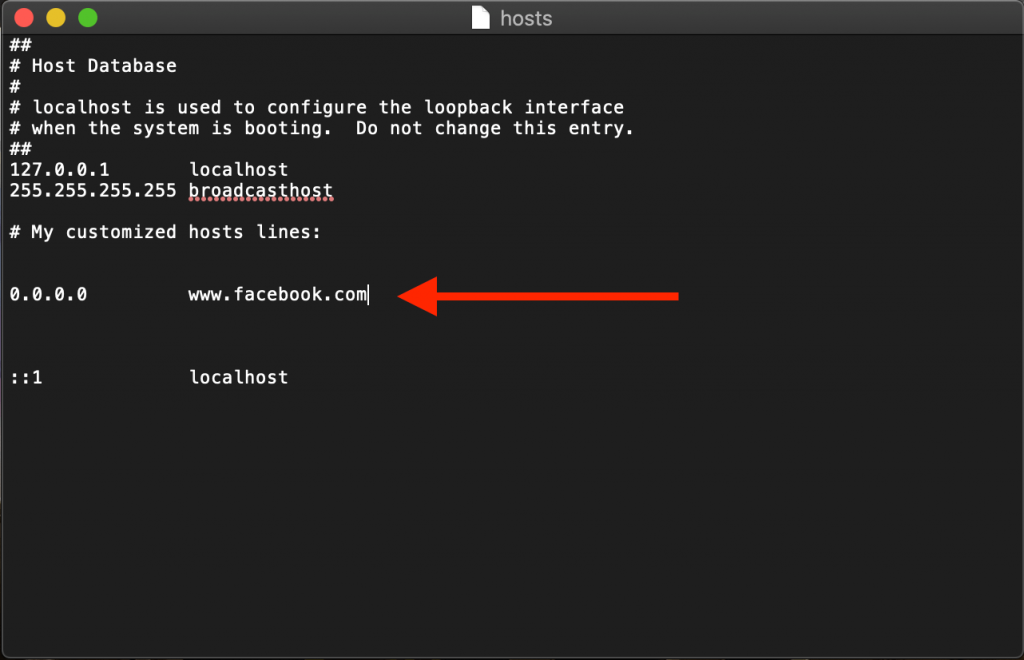 11 Best Free VPN For Mac in 2021Looking for privacy and security while surfing internet on Mac, then check out the free and best VPN services for... How to Edit Hosts File on Mac with TextEditHosts File ExamplesAnother way for editing hosts file on Mac is via apart from using Mac terminal text editor is TextEdit.
Hosts File Mac TerminalBest Security Tips And Tricks To Secure Your...Read this to know how you can secure your Mac as it is important to keep it in mind if... Hosts File MacSo folks, here was a quick guide on how to edit Mac hosts file! We hope the above mentioned steps will help you in getting through! Hosts File Macos CatalinaFor any other queries or feedback feel free to hit the comment box! |